
When we talk about arthritis, the first things that come to mind are hip and knee arthritis , but it should not be forgotten that arthritis can also occur in other joints in our body. Facet joint arthritis in the lumbar (lower back) spine is one of them and is commonly known as “lower back arthritis .” Although disc degeneration is considered the most common cause of back pain, research on this subject emphasizes that 15-45% of back pains are caused by lumbar arthritis and it is especially more common in women.
If you are experiencing back pain or pain radiating from your back to your leg, you can find the answers to the questions: What is lower back Arthritis? What are the symptoms of lower back Arthritis? What causes lower back Arthritis and what helps withlower back Arthritis ? in the continuation of our article.
Table of Contents:
- What is lower back Arthritis?
- What Are the Symptoms of Lumbar Arthritis?
- What Causes Lumbar Arthritis?
- Diagnosing Lumbar Arthritis: How Is It Done?
- Treatment for Lumbar Arthritis: What Helps with Lumbar Arthritis ?
What is lower back Arthritis?
Lower back Arthritis, in its simplest definition, is the calcification that occurs between two vertebrae and in the facet joints of the lumbar spine as a result of wear and tear.
The facet joints, located at the back of the spine, are present on the right and left sides at each level of the spine, providing the connection between the vertebrae (Figure 1). The primary function of these joints is to stabilize the spine during bending and twisting movements and to prevent the slipping of spinal bodies.
However, when the protective cushioning cartilage tissue between the facet joints wears away, narrowing of the joint space and joint damage occur. The degenerated facet joint grows outward to compensate for the lost cartilage and forms new bony projections called “osteophytes.”
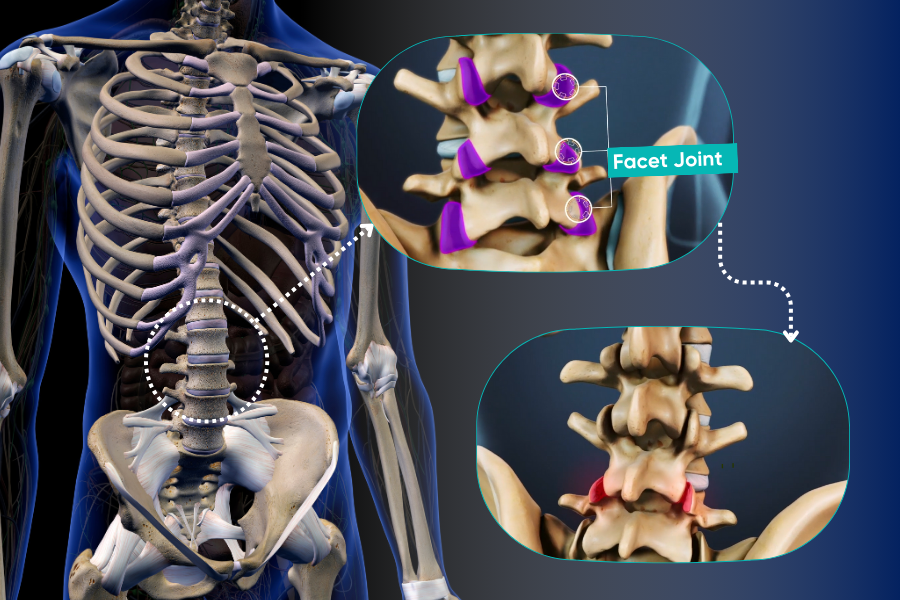
Usually, calcification in the facet joint and narrowing and calcification of the joint between the lumbar vertebrae occur together. All these changes in the lumbar region are referred to as “lower back Arthritis .“
What Are the Symptoms of Lumbar Arthritis ?
The symptoms of lower back Arthritis vary depending on the severity of the condition. However, the most typical symptom of lumbar arthritis is pain and stiffness in the joints. These pains can radiate from the back to the buttocks, thighs, groin, and legs, and may also be felt in the abdomen and/or pelvic bone. (Figure 2).
Pain associated with lower back Arthritis typically increases in the mornings, after prolonged periods of inactivity, following intense exercise, and when standing or bending the spine backward. For example, prolonged sitting, such as driving a car or long bus journeys, can exacerbate the pain.

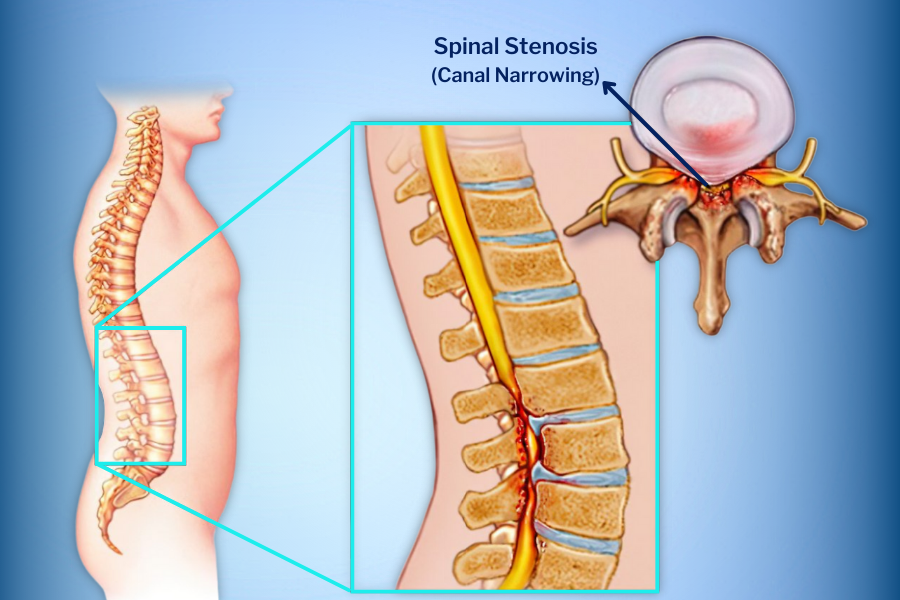
Additionally, the growth of bone projections in the facet joint can compress the nerves or nerve roots in the spinal cord, causing narrowing of the spinal canal, known as spinal stenosis. In this case, you may experience pain (sciatica pain) radiating from your lower back to your hips and legs, as well as symptoms such as tingling or numbness. Therefore, early detection of lumbar arthritis symptoms is crucial.
What Causes Lumbar Arthritis ?
There are various factors that can cause lower back arthritis .These include:
Age
One of the most significant causes of lumbar arthritis is the wear and tear of cartilage tissue in the joints over time due to aging. Therefore, the likelihood of lower back arthritis is higher, especially in people aged between 40 and 70.
Disk Degeneration
Lower back arthritis can also occur due to the decrease in intervertebral disc height between the vertebrae (disk degeneration). As the height of the discs decreases, the pressure on the facet joints increases. This, in turn, leads to the wearing away of cartilage tissue between the joints.
Trauma and Injuries
Injuries and strains that change the alignment and movement pattern of the facet joints can cause degeneration and calcification of the facet joints.
Obesity
Obesity, i.e. obesity and abdominal fat, is another factor that can cause arthritis . Studies have shown that abdominal fat, in particular, increases the risk of arthritis .
Postural Reasons
The load sharing of the disc and facet joints varies according to the position of the spine. When standing upright, 70% of the body weight is transferred to the intervertebral discs and 30% to the facet joints. However, calcification can also be seen as a result of increased load on the facet joints due to posture disorder.
Diagnosing Lumbar arthritis : How Is It Done?
The pain in lower back arthritis can be similar to pain associated with other spinal degenerations. A correct diagnosis is very important to determine whether the source of your pain is arthritis of the lower back.
The diagnosis of arthritis includes the patient’s medical history and physical examination. After the physical examination, imaging methods such as X-ray, Computed Tomography (CT) or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) will be used to help the diagnosis.
In addition, a diagnostic facet joint block injection is often performed to confirm the cause of the pain. In a diagnostic facet joint block injection, a drug containing local anesthetic and cortisone is injected into the problematic facet joint in the lower back. This is done with the help of an X-ray device called fluoroscopy so that the injection can be administered correctly into the facet joint.
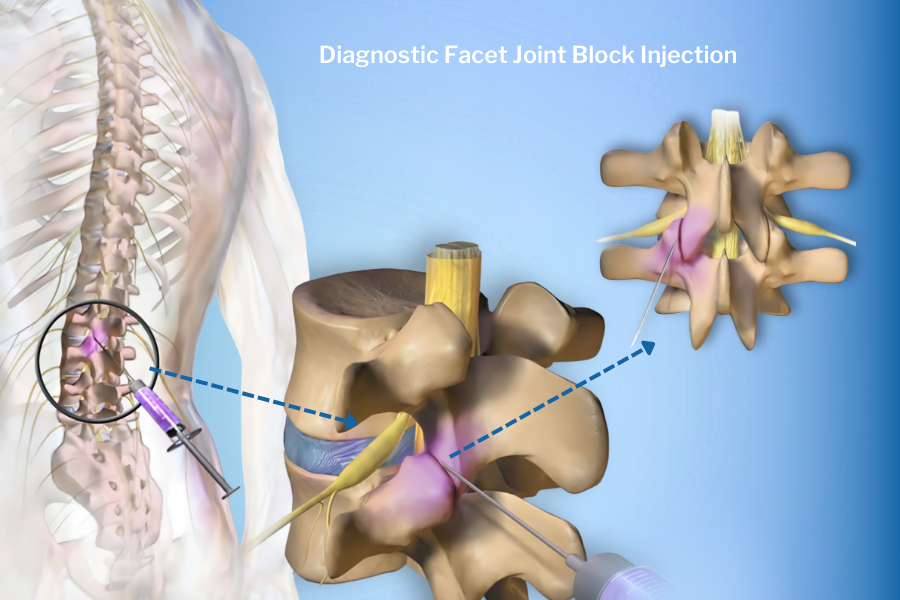
The patient’s pain level is evaluated before and 20-30 minutes after the diagnostic facet joint block injection. If the pain level decreases after the injection, it confirms that the pain is originating from the facet joint, and the treatment process begins.
Treatment for Lumbar arthritis : What Helps with Lumbar arthritis ?
Lower back arthritis is an irreversible condition. However, controlling the pain associated with lumbar arthritis can be achieved through non-surgical treatment options. The surgical option for lower back arthritis is generally considered when it is expected to lead to other spinal conditions (spinal stenosis).
The methods applied in the treatment of lower back arthritis are as follows:
Medications
For the pain caused by lower back arthritis , analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antidepressants, or muscle relaxants for muscle spasms can be prescribed.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy and exercises are highly effective in treating lower back arthritis pain. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the patient’s back, leg, and abdominal muscles.
Additionally, pain relief through hot-cold therapy, correction of posture, keeping the spine aligned, and weight management through exercise can also alleviate pain by reducing the load on facet joints.
Facet Joint Injections
Facet joint injection is a procedure that involves the injection of corticosteroids and analgesic substances into the painful joint. Injections applied directly to the facet joint can provide relief from back pain within a short time and may offer comfort for several months.
However, in some cases, a block injection is applied to the nerve branch responsible for transmitting the pain rather than directly into the facet joint. Facet joint injections can be repeated if the pain recurs. However, the number of injections that can be administered within a year is limited due to the use of corticosteroids.

Radiofrequency Ablation (Facet Joint Denervation)
The nerve responsible for transmitting pain originating from facet joints is referred to as the “medial branch.” In the radiofrequency ablation method, under the guidance of ultrasound or fluoroscopy, needles and electrodes are used to apply radiofrequency current to the medial branches. With these electrodes, controlled heat is applied to the nerves, effectively interrupting nerve conduction, and thus pain transmission.
As a result, the patient no longer feels the pain caused by the issue in the joint. The procedure takes approximately 25-30 minutes. The effectiveness varies from person to person but typically lasts between 6 months to 1 year.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered in cases of advanced lower back arthritis leading to spinal stenosis when non-surgical treatment options are not sufficient. Surgery is often viewed as a concerning option for many patients. However, with modern robotic spine surgery techniques used in leading clinics around the world, it is possible to mitigate the complications that patients may experience during and after surgery.

The most effective method used worldwide to reduce pain in the treatment of lower back arthritis is radiofrequency ablation, also known as facet joint denervation. This treatment option is particularly applied to patients who have shown positive results with facet joint blocks. However, if you are experiencing pain that is making your daily life difficult due to lower back arthritis, the most suitable treatment option for you will be determined by a Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation or Orthopedics and Traumatology specialist doctor.
To obtain more detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of lower back arthritis, you can contact us and send us the X-rays or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) images you recently had to get an expert opinion.








Leave a Comment