
Do you experience wrist pain when picking up objects such as teapots in your daily life? Do you feel like you’re losing your grip when you hold a coffee cup? Do you experience hand numbness that wakes you up at night? These symptoms may be caused by carpal tunnel syndrome, a common condition involving nerve compression in the hand.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is usually characterized by pain in the wrist and numbness and tingling in the fingers. However, you should consult a doctor if the symptoms affect your daily activities and sleeping schedule. If left untreated, carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to permanent nerve and muscle damage, resulting in numbness and weakness in the hand.
Table of Contents
- What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
- What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
- What are the Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
- How is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed?
- What are the Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
- Non-Surgical Treatment Options
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Pregnancy
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the medical term for a pinched nerve in the hand. The wrist joint has a narrow, tunnel-like canal that is lined with bones on one side and connective tissue on the other. This channel is called the “carpal tunnel.” The median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel and controls the movement and sensation of the fingers, especially the first three. Narrowing of the carpal tunnel puts pressure on the median nerve, causing symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand. This condition is known as carpal tunnel syndrome.

What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The exact cause of nerve compression in the hand is unknown, but certain conditions may contribute to it. Age and gender, in particular, are risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome. The carpal tunnel is narrower in women than in men. Therefore, nerve compression is more common in women.
Some of the causes and risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome are as follows:
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- Wrist fractures,
- Rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,
- Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid gland),
- Mass formation in the carpal tunnel,
- Repetitive hand-wrist movements at home, at work, or during sports activities,
- Use of vibrating tools or machines at work.
What are the Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome typically develop gradually. Over time, the symptoms become more pronounced and progressively worsen. Symptoms of a pinched nerve in the hand typically manifest as one or more of the following:

- Burning, tingling, or numbness in the palm, especially in the thumb, index finger, and middle finger.
- Hand and wrist pain or a tingling sensation that wakes you at night and is partially relieved by shaking your hand.
- Numbness and tingling when holding the wrist in a fixed position, such as when driving a car or reading a book;
- Pain radiating from the wrist up to the arm;
- Difficulty holding or grasping objects due to weakness in the hands and fingers.
- Numbness and tingling that occurs with repetitive movements, such as knitting or painting.
- In advanced cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, the muscle on the palm side of the thumb appears collapsed due to weakening.
The symptoms of a pinched nerve in the hand are quite distinctive. However, other neuropathies (nerve disorders) or degenerative conditions, such as hand osteoarthritis, can cause similar symptoms. To determine the appropriate treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome, a doctor must examine and evaluate the patient.
How is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed?
To the diagnose the nerve compression in the hand (carpal tunnel syndrome), patient’s complaints and medical history must first be obtained. It is important for doctors to know about the onset and duration of the complaints, the conditions that increase the complaints and other medical conditions, if any. The patient is then examined in detail.
To clarify the diagnosis, some tests specific to carpal tunnel syndrome are asked. These tests check progression of the symptoms. Motor and sensory examination is used to check for muscle weakness and sensory deficits in the hand. If physical examination supports the suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome, electrophysiological tests are used to confirm the diagnosis. Electromyography, also known as EMG, is performed. This diagnostic method determines the degree of nerve compression in the carpal tunnel by measuring nerve conduction velocities and assessing muscle strength. Since some other nerve and muscle diseases can also be detected during EMG, it is a guide in differential diagnosis.

It is important to differentiate carpal tunnel syndrome from pain caused by a herniated disc in the cervical spine or some other shoulder or elbow conditions. If the patient has complaints about these areas other than the wrist, it is useful to evaluate these areas with radiological imaging methods such as X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound in order to determine the actual source of the problem. In cases where carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by a rheumatic disease, diabetes or goiter, various blood tests are required.
What are the Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Various surgical and non-surgical treatment options are available for carpal tunnel syndrome, which can relieve pain in the hand and numbness in the fingers. Depending on your symptoms and the severity of nerve compression, you will receive the appropriate treatment. The goal of treating carpal tunnel syndrome is to reduce and eliminate the conditions that cause compression and damage to the median nerve in the carpal tunnel.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Some non-surgical treatment methods for carpal tunnel syndrome include:
Rest: Taking a break from repetitive movements that strain the wrist will alleviate numbness and pain.
Medication use: : Various medications are used to reduce pain caused by nerve compression. However, it is important to remember that medication does not address the underlying problem. Medications can be used short-term according to a doctor’s recommendation.

Using a wrist brace: A wrist splint keeps the wrist in a natural position during daily activities and while sleeping. It keeps the wrist and surrounding muscles, ligaments, and joints in the ideal position. Thus, there is less pressure on the tendons and nerves passing through the carpal tunnel, which reduces complaints. You may be recommended to wear the brace for a few weeks during the day and at night.
Cold application: One method used to treat carpal tunnel syndrome is cold application. The cold helps reduce swelling and relieve wrist pain. Cold applications can be done three to four times a day for 15 to 20 minutes. To avoid a rash-like reaction to the cold, make sure there is no direct contact between the ice and your skin. You can apply the cold pack by wrapping it in a thin towel or sheath.

Making changes in daily life: Although carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms can be managed with various methods, patients may need to change their daily habits to prevent recurrence. Those who use vibrating tools, such as drills, should take more frequent breaks from work. Office workers should use ergonomic keyboards and supportive mouse pads when using computers.
Injection treatment for carpal tunnel: When rest, wrist braces, cold applications, and medication do not relieve symptoms, injection therapy may be recommended.
Physical therapy and exercise: Patients diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome are recommended a program of physical therapy and exercises along with non-surgical treatments. In addition, if necessary, a physical therapy program is provided after the operation to increase nerve mobility and enable patients to use their hands comfortably.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery
Not all patients with carpal tunnel syndrome require surgery. Surgery becomes an option when non-surgical treatments fail to relieve symptoms, especially for patients with progressive symptoms or muscle mass loss around the thumb due to nerve compression.
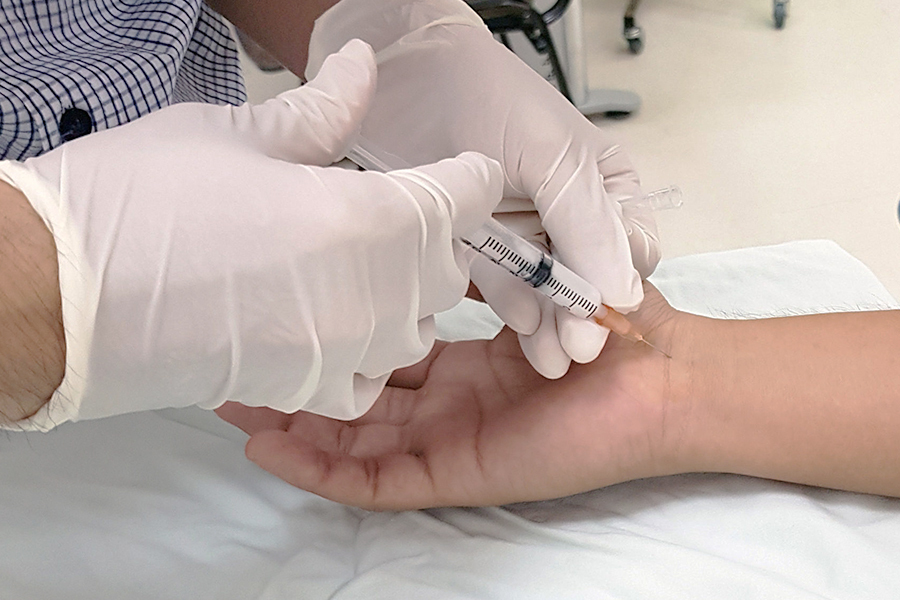
During surgery, an incision approximately 3-4 centimeters long is made on the front side of the wrist. Then, the connective tissue forming the upper wall of the carpal tunnel is loosened to allow free movement of the structures passing through the tunnel.

This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, and patients can go home the same day. The stitches are removed after 10–15 days. Once the stitches have been removed, it is recommended that the area be softly massaged to prevent stiffness at the wound site, and an exercise program is given to regain the range of motion in the wrist.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Pregnancy
In the later stages of pregnancy, usually from the sixth month onward, excess fluid accumulates in the body. This excess fluid, known as edema, manifests as swelling in the hands and feet. It creates pressure in the carpal tunnel in the wrist, compressing the structures passing through it. This compression of the median nerve causes symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and fingers.
As edema decreases after birth, the pressure in the carpal tunnel decreases, and symptoms usually disappear. Surgery is rarely required. Non-surgical methods to reduce symptoms until birth include resting, using wrist braces, applying cold, doing appropriate exercises, and avoiding movements that require bending the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome may occur for many reasons and may cause different symptoms. You can visit our clinic to confirm your diagnosis and evaluate your treatment options. Feel free to contact us with any questions or comments.








Leave a Comment